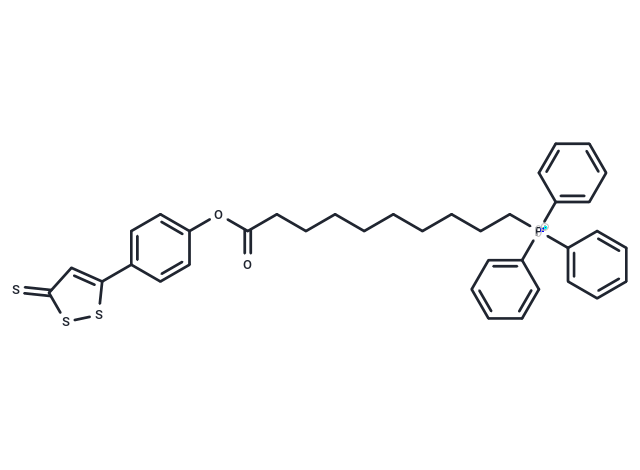
AP39 Free base
CAS No. 1429173-57-8
AP39 Free base( —— )
Catalog No. M34796 CAS No. 1429173-57-8
AP39 free base is a mitochondrial-targeted H(2)S donor that can improve the survival rate of porcine islets in culture.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 53 | Get Quote |


|
| 5MG | 77 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 132 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 266 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 456 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameAP39 Free base
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionAP39 free base is a mitochondrial-targeted H(2)S donor that can improve the survival rate of porcine islets in culture.
-
DescriptionAP39 free base is a mitochondrial-targeted H(2)S donor that can improve the survival rate of porcine islets in culture. AP39 free base regulates mitophagy through the AMPK-ULK1-FUNDC1 pathway, inhibits cell pyroptosis, and improves doxorubicin-induced myocardial fibrosis.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1429173-57-8
-
Formula Weight641.87
-
Molecular FormulaC37H38O2PS3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESO=C(OC=1C=CC(=CC1)C=2SSC(=S)C2)CCCCCCCCC[P+](C=3C=CC=CC3)(C=4C=CC=CC4)C=5C=CC=CC5
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
PI-55
PI-55 (6-(2-hydroxy-3-methylbenzylamino)purine) is a cytokinin receptor inhibitor that exhibits structural similarity to 6-benzylaminopurine (BAP).
-
Thionin acetate
Thionin acetate is a metachromatic cationic histology dye used in biological staining widely.
-
α-Ketoglutaric acid ...
alpha-Ketoglutarate is a key molecule in the TCA cycle. It can be produced from glutamate by oxidative deamination via glutamate dehydrogenase and as a product of pyridoxal phosphate-dependent transamination reactions (mediated by branched-chain amino acid transaminases) in which glutamate is a common amino donor.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


